B.Tech (Civil) Syllabus
Semester IV
-
COURSE CODECOURSE NAMECREDITS
-
JEOE-041-048 /JEAS-401
Science Based Open Elective/Engineering Mathematics III
Introduction to Soft Computing (JEOE-041):
UNIT-I
Neural Networks-1(Introduction & Architecture) Neuron, Nerve structure and synapse, Artificial Neuron and its model, activation functions, Neural network architecture: single layer and multilayer feed forward networks, recurrent networks, Various learning techniques; perception and convergence rule, Auto-associative and hetro-associative memory.
UNIT-II
Neural Networks-II (Back propogation networks) Architecture: perceptron model, solution, single layer artificial neural network, multilayer perception model; back propogation learning methods, effect of learning rule co-efficient ;back propagation algorithm, factors affecting backpropagation training, applications.
UNIT-III
Fuzzy Logic-I (Introduction) Basic concepts of fuzzy logic, Fuzzy sets and Crisp sets, Fuzzy set theory and operations, Properties of fuzzy sets, Fuzzy and Crisp relations, Fuzzy to Crisp conversion.
UNIT-IV
Fuzzy Logic II (Fuzzy Membership, Rules) Membership functions, interference in fuzzy logic, fuzzy if-then rules, Fuzzy implications and Fuzzy algorithms, Fuzzy fications & Defuzzi ficataions, Fuzzy Controller, Industrial applications.
UNIT-V
Genetic Algorithm(GA): Basic concepts, working principle, procedures of GA, flow chart of GA, Genetic representations, (encoding) Initialization and selection, Genetic operators, Mutation, Generational Cycle, applications.
Books:
- 1. S. Rajsekaran & G.A. Vijayalakshmi Pai, “Neural Networks,Fuzzy Logic and Genetic
- 2. Algorithm:Synthesis and Applications” Prentice Hall of India.
- 3. N.P.Padhy,”Artificial Intelligence and Intelligent Systems” Oxford Univ. Press
- 4. Siman Haykin,”Neural Netowrks”Prentice Hall of India
- 5. Timothy J. Ross, “Fuzzy Logic with Engineering Applications” Wiley India.
Nano Sciences (JEOE-042):
UNIT-I
Introduction: Definition of Nano-Science and Nano Technology, Applications of Nano Technology, Introduction to Physics of Solid State: Structure: Size dependence of properties; crystal structures, face centred cubic, nano particles; Tetrahedrically bounded semiconductor structures; lattice vibrations. Energy Bands: Insulators, semiconductor and conductors; Reciprocal space; Energy bands and gaps of semiconductors; effective masses; Fermi Surfaces. Localized Particles: Acceptors and deep taps; mobility; Excitons.
UNIT-II
Quantum Theory For Nano Science: Time dependent and time independent Schrodinger wave equations. Particle in a box, Potential step: Refelection and tunneling (Quantum leak). Penetration of Barrier, Potential box (Trapped particle in 3D: Nanodot), Electron trapped in 2D plane (Nano sheet), Quantum confinerment effect in nano materials. Quantum Wells, Wires and Dots Preparation of Quantum Nanostructure; Size and Dimensionality effect, Fermigas: Potential wells; Partial confinement: Excitons: Single electron Tunneling, Infrared etectors: Quantum dot laser Superconductivity, Properties of Individual Nano particlesMetal Nano clusters: Magic Numbers; Theoretical Modelling of Nanopraticles; geometric structure; electronic structure; Reactivity; Fluctuations Magnetic Clusters; Bulle to Nano structure. Semi conducting Nanoparticles: Optical Properties; Photofragmentation; Coulmbic explosion. Rare Gas & Molecular Clusters: Inert gas clusters; Superfluid clusters molecular clusters.
UNIT-III
Growth Techniques of Nanomaterials: Lithograpahic and Nonlithograpahic techniques, Sputtering and film deposition in glow discharge, DC sputtering technique (p-CuAlO2 deposition), Thermal evaporation technique, E-beam evaporation, Chemical Vapour deposition(CVD), Synthesis of carbon nano-fibres and multi-walled carbon nanotubes, Pulsed Laser Deposition, Molecular beam Epitoxy, Sol-Gel Techniuqe (No chemistry required), Synthesis of nanowires/rods, Electrodeposition, Chemical bath deposition, Ion beam deposition system, Vapor-Liquid –Solid (VLS) method of nanowires.
UNIT-IV
Methods of Measuring Properties: Structure: Crystallography, particle size determination, surface structure, Microscopy: Scanning Prob Microscopy (SPM), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), Field Ion Microscopy, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Transmission Elecrtron Microscopy (TEM)Spectroscopy: Infra red and Raman Spectroscopy, X-ray Spectroscopy, Magnetic Resonance, Optical and Vibrational Spectroscopy, Luninscence.
UNIT-V
Buckey Ball: Nano structuresof carbon (fullerene): Carbon nano-tubes: Fabrication, structure, Electrical, mechanical, and vibrational properties and applications. Nano diamond, Boron Nitride Nano-tubes, single elecron transistors, Moelcular machine, Nano-Biometrics, Nano Robots
Books:
- 1. C.P.Poole Jr F.J. Owens, “Introduction to Nanotechnology”.
- 2. “Introduction to S.S. Physics” Wiley 1996.
- 3. S. Sugano & H. Koizuoni, “Microcluster Physics” –Springor 1998
- 4. “Handboole of Nanostructured Materials & Nanotechnology” vol.-5.
- 5. A.K.Bandyopadhyay, “Nano Materials” New Age International.
Laser Systems and Applications (JEOE-043):
UNIT-I & II
Introduction: Review of elementary quantum physics, Schrodinger equation, concept of coherence, absorption, spontaneous emission and stimulated emission processes, relation between Einstein’s A and B coefficients, population inversion, pumping, gain, optical cavities.
UNIT-III & IV
Lasers & Laser Systems: Main components of Laser, principle of Laser action, introduction to general lasers and their types. Three & four level Lasers, CW & Pulsed Lasers, atomic, ionic, molecular, excimer, liquid and solid state Lasers and systems, short pulse generation and Measurement.
UNIT-V
Applications: Laser applications in medicine and surgery, materials processing, optical communication, metrology and LIDAR and holography.
Books:
- 1. KR Nambiar, “Laser Principles, Types & Application” New Age International
- 2. S. A. Ahmad, “Laser concepts and Applications” New Age International
Space Sciences (JEOE-044):
UNIT-I
Introduction: Introduction to space science and applications, historical development
UNIT-II
Solar System: Nebular theory of formation of our Solar System, Solar wind and nuclear reaction as the source of energy. Sun and Planets: Brief description about shape size, period of rotation about axis and period of revolution, distance of planets from sun, Bode’s law, Kepler’s Laws of planetary motion, Newton’s deductions from Kepler’s Laws, Newton’s Law of gravitation, correction of Kepler’s third law, determination of mass of earth, determination of mass of planets with respect to earth, Brief description of Asteroids, Satellites and Comets.
UNIT-III
Stars: Stellar spectra and structure, stellar evolution, nucleo-synthesis and formation of elements. Classification of stars: Harvard classification system, Hertzsprung-Russel diagram, Luminosity of star, variable stars; composite stars (white dwarfs, Neutron stars, black hole, star clusters, supernova and binary stars); Chandrasekhar limit.
UNIT-IV
Galaxies: Galaxies and their evolution and origin, active galaxies and quasars.
UNIT-V
Creation of Universe: Early history of the universe, Big-Bang and Hubble expansion model of the universe, cosmic microwave background radiation, dark matter and dark energy.
Books:
- 1. K.S. Krishnaswami, Astrophysics: A modern Perspective, N. A. International.
- 2. K.S. Krishnaswami, Understanding cosmic Panorama, New Age International.
Polymer Science and Technology (JEOE-045):
UNIT-I & II
POLYMERS: Introduction, chemistry of polymer synthesis, polymer reaction kinetics, physical properties and characterization of polymers, effect of structure on properties of polymers, organic polymers, Introduction to high performance polymers and composites and their processing.
UNIT-III & IV
POLYMERIZATION: Introduction, step-growth polymerization, free radical chain growth polymerization, emulsion polymerization, ionic and cationic polymerization, chain statistics and rubber elasticity.
UNIT-V
PREPARATION AND APPLICATIONS: Preparation, properties and technical applications of thermo-plastics (PVC, PVA), thermostats (PF, UF) and elastomers (SBR, GR-N), silicones, Application of polymers in space, ocean, electronics, medical, agriculture, automobile, sports and building construction.
Nuclear Science (JEOE-046):
UNIT-I
Nucleus and Its Basic Features: Nuclear structure; nuclear forces and their properties, nuclear stability, nuclear radius and its meassurement, nuclear spin, nuclear magnetic and electrical moments.
UNIT-II
Nuclear Models: Single particle model, liquid drop model and semi-emperical mass formula, nuclear potential and shell model, collective model.
UNIT-III
Nuclear Reaction: Nuclear reaction and laws of conservation, types of nuclear reaction, mechanism of nuclear reaction, nuclear fission & binuclear fusion and their explanation by liquid drop model.
UNIT-IV
Nuclear Decay: Decay constant, half life period and mean life, alpha decay, beta decay, gamma decay, interaction of nuclear radiation with matter, Nuclear Instruments-I Mass spectrograph: General principle, Aston’s Mass Spectrograph.
UNIT-V
Nuclear Instruments-II Accelerators: Van de Graph Generator, Cyclotron, Synchrotron. Detectors: G M Counter, Scintillation counter, cloud chamber, Bubble Chamber, production and detection of neutrons and Gamma-photon. Application of Nuclear Techniques: Nuclear magnetic resonance, positron emission topography, radiotracer techniques and applications in material science and agriculture.
Books:
- 1. Tayal, “Nuclear Physics” Himalaya Publishing House.
- 2. S.N. Ghosal, “Nuclear Physics” S. Chand & Co
- 3. S. B. Patel, “Nuclear Physics: An Introduction New Age International.
- 4. H. B. Lal, “Introuctory Nucler Physics” United Book Depot.
- 5. Wang, “Introductory Nuclear Physics”, PHI Learning
- 6. Roy & Nigam, “Nuclear Physics” John Wiley & sons.
- 7. W.E. Burcham, “Nuclear Physics” Longmans Publications.
- 8. Green, “Nuclear Physics” McGraw Hill
Material Science (JEOE-047):
UNIT-I
Introduction: Historical perspective, importance of materials, Brief review of modern & atomic concepts in Physics and Chemistry. Atomic models, Periodic table, Chemical bonding. Crystallography and imperfections: Concept of unit cell, space lattice, Bravais lattices, common crystal structures, Atomic packing factor and density, Miller indices X-ray crystallography techniques, imperfections, Defects & Dislocations in solids.
UNIT-II
Mechanical Properties and Testing: Stress strain diagram, Ductile and brittle materials, stress Vs strength, toughness, hardness, fracture, fatigue and creep, Testing, such as Strength testing, Hardness testing, Impact testing, Fatigue testing Creep testing, Non-destructive testing (NDT) Micro Structural Exam: Microscope principle and methods, Preparation of samples and microstructure exam and grain size determination, comparative study of microstructure of various metals and alloys, such as Mild steel, CI, Brass. Phase Diagram and Equilibrium Diagram: Uniary and Binary diagrams, Phase rules, Types of equilibrium diagrams: solid solution type, eutectic type and combination type, Iron-carbon equilibrium diagram.
UNIT-III
Ferrous materials: Iron and steel manufacture, furnaces, various types of carbon steels, alloy Steels and cast irons, its properties and uses, Heat Treatment: various types of heat treatment, such as Annealing, Normalizing, Quenching, Tempering and Case hardening. Time Temperature Transformation (TTT) diagrams, Non-Ferrous metals and alloys: Non-ferrous metals, such as Cu, Al, Zn, Cr, Ni etc. and its applications, Various types of Brass, Bronze bearing materials their properties and uses, Aluminum alloys, such as Duralumin, Other advanced materials/alloys.
UNIT-IV
Magnetic properties: Concept of magnetism- Dia, para, ferro magnetic materials, Hysteresis, Soft and hard magnetic materials, Magnetic Storages, Electric Properties: Energy band, concept of conductor, insulator and semi conductor, Intrinsic and extrinsic semi-conductors, P-n junction and transistors, Basic devices and their applications, diffusion of Solid Super conductivity and its applications, Messier effect. Type I & II superconductors, High Temp superconductors
UNIT-V
Ceramics: Structure, types, properties and applications of ceramics. Mechanical/Electrical behaviour and processing of ceramics, Plastics: Various types of polymers/plastics and their applications, Mechanical behaviour and processing of plastics, Future of plastics, Other Materials: Brief description of other materials, such as optical and thermal materials, concrete, composite materials and their uses, Other Materials: Brief description of other materials, such as optical and thermal materials, concrete, composite materials and their uses, Performance of materials in service: Brief theoretical consideration of fracture, fatigue, and Corrosion and its control
Books:
- 1. W.D. Callisster Jr. “Material Science & Engineering Addition” - Wesly Publishing Co.
- 2. Van Vlash, “Elements of Material Science & Engineering”, John Wiley & Sons
- 3. V. Raghvan, “Material Science”, Prentice Hall of India
- 4. Narula, “Material Science”, Tata Mc.Graw Hill
- 5. Srivastava, Srinivasan, “Science of Materials Engineering” N. A. International.
Discrete Mathematics (JEOE-048):
UNIT-I
Set Theory: Definition of Sets, Venn Diagrams, complements, cartesian products, power Sets counting principle, cardinality and countability (Countable and Uncountable sets), Proof of some general identitites on sets, pigeonhole principle, Relation: Definition, types of relation, composition of relations, domain and range of a relation, pictorial representation of relation, properties of relation, partial ordering relation. Function: Definition and types of function, composition of functions, recursively defined functions.
UNIT-II
Propositional logic: Proposition logic, basic logic, logical connectives, truth tables, tautologies, contradiction , normal forms(conjunctive and disjunctive), modus ponens and modus tollens, validity, predicate logic, universal and existential quantification, Notion of proof: proof by implication, converse, inverse, contrapositive, negation, and contradiction, direct proof, proof by using truth table, proof by counter example.
UNIT-III
Combinatories: Mathematical induction, recursive mathematical definitions, basics of counting, permutations, combinations, inclusion-exclusion, recurrence relations (nth Order recurrence relation with constant coefficients, Homogeneous recurrence relations, Inhomogeneous recurrence relation), generating function (closed form expression, properties Of G.F., solution of recurrence relation using G.F, solution of combinatorial problem using G.F)
UNIT-IV
Algebraic Structure: Binary composition and its properties definition of algebraic structure; Groyas Semi group, Monoid Groups, Abelian group, properties of groups, Permutation Groups, Sub Group, Cyclic Group, Rings and Fields (definition and standard results)
UNIT-V
Graphs: Graph terminology, types of graph connected graphs, components of graph, Euler graph, Hamiltonian path and circuits, Graph coloring, Chromatic number. Tree: Definition, types of tree (rooted, binary), properties of trees, binary search tree, tree traversing (preorder, inorder, postorder), Finite Automata: Basic concepts of Automation theory, Deterministic finite Automation(DFA), transition function, transition table, Non Deterministic Finite Automata (NDFA), Mealy and Moore Machine, Minimization of finite Automation.
Books:
- 1. Kenneth H. Rosen, “Discrete Mathematics and its Applications”, McGraw Hill, 2002
- 2. J.P. Tremblay & R. Manohar, “Discrete Mathematical Structure with Applications to Computer Science” McGraw Hill.
- 3. V. Krishnamurthy, “Combinatories: Theory and Applications”, East-West Press.
- 4. Seymour Lipschutz, M.Lipson, “Discrete Mathematics” Tata McGraw Hill.
- 5. Kolman, Busby Ross, “Discrete Matheamatical Structures”, Prentice Hall International.
Engineering Mathematics III (JEAS-401):
UNIT-I
Function of Complex variable: Analytic function, C-R equations, Cauchy’s integral theorem, Cauchy’s integral formula for derivatives of analytic function, Taylor’s and Laurent’s series, singularities, Residue theorem, Evaluation of real integrals of the type
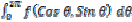 and
and 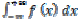
UNIT-II
Statistical Techniques – I: Moments, Moment generating functions, Skewness, Kurtosis, Curve fitting, Method of least squares, Fitting of straight lines, Polynomials, Exponential curves etc., Correlation, Linear, non –linear and multiple regression analysis, Probability theory.
UNIT-III
Statistical Techniques – II: Binomial, Poisson and Normal distributions, Sampling theory (small and large), Tests of significations: Chi-square test, t-test, Analysis of variance (one way) , Application to engineering, medicine, agriculture etc.Time series and forecasting (moving and semi-averages), Statistical quality control methods, Control charts, X , R, p, np, and c charts.
UNIT-IV
Numerical Techniques – I: Zeroes of transcendental and polynomial equation using Bisection method, Regula-falsi method and Newton-Raphson method, Rate of convergence of above methods.Interpolation: Finite differences, difference tables, Newton’s forward and backward interpolation, Lagrange’s and Newton’s divided difference formula for unequal intervals.
UNIT-V
Numerical Techniques –II: Solution of system of linear equations, Gauss- Seidal method, Crout method. Numerical differentiation, Numerical integration , Trapezoidal , Simpson’s one third and three-eight rules, Solution of ordinary differential (first order, second order and simultaneous) equations by Euler’s, Picard’s and forth-order Runge- Kutta mehthods.
Books:
- 1. Peter V. O’Neil, Advance Engineering Mathematics Thomson (Cengage) Learning.
- 2. Jain, Iyenger & Jain, Numerical Methods for Scientific and Engineering Computation, New Age International, New Delhi, 2003.
- 3. J.N. Kapur, Mathematical Statistics, S. Chand & company Ltd.
- 4. R.K. Jain & S.R.K. Iyenger, Advance Engineering Mathematics, Narosa Publication House, 2002.
- 5. Chandrika Prasad, Advanced Mathematics for Engineers, Prasad Mudralaya.
- 6. E. Kreysig, Advanced Engineering Mathematics, John Wiley & Sons, 2005.
- 7. B.S. Grewal, Higher Engineering Mathematics, Khanna Publishers, 2005.
- 8. Devi Prasad, An introduction to Numerical Analysis, Narosa Pub. House, ND.
04 -
JECE-401
Fluid Mechanics:
UNIT-I
Classification of Structures, stress resultants, degree of freedom per node, Static and Kinematic determinacy .Classification of Pin jointed determinate trusses, Analysis of determinate plane truss. Method of joint and method of section.
UNIT-II
Rolling loads, influence lines for beams and trusses, Absolute maximum bending moment, Muller-Breslau’s principal & its application for determinate structures.
UNIT-III
Analysis of Arches, Linear arch, Eddy’s theorem, three hinged parabolic arch, spandrel braced arch, moving load & influence lines.
UNIT-IV
Strain Energy of deformable systems, Maxwell’s reciprocal & Betti’s theorem, Castigliano’s first theorem, unit load & moment area method and Conjugate beam methods.
UNIT-V
Plastic analysis: Introduction, plastic hinge concept, plastic modulus, shape factor, load factor, Upper and lower bound theorems, collapse mechanisms, combined mechanism, plastic analysis of beams and portal frames by equilibrium and mechanism methods.
Books:
- 1. Structure Analysis by B.C. Punmia
- 2. Hibbler, “Structural Analysis”, Pearson Education
- 3. Reddy, C.S., “Basic Structural Analysis”, Tata McGraw Hill.
- 4. T S Thandavmorthy, “Analysis of Structures”, Oxford University Press
- 5. Wilbur and Norris, “Elementary Structural Analysis”, Tata McGraw Hill.
- 6. Jain, O.P. and Jain, B.K., “Theory & Analysis of Structures”. Vol I & II Nem Chand.
- 7. Vazirani & Ratwani et al, “Analysis of Strcuctures”, Khanna Publishers
- 8. Coates, R.C., Coutie, M.G. & Kong, F.K., “Structural Analysis”, English Language Book Society & Nelson, 1980.
04 -
JECE-402
Geoinformatics:
UNIT-I
Aerial Photographs- Basic terms & Definitions, scales, relief displacements, Flight Planning, Stereoscopy, Characteristics of photographic images, Fundamentals of Aerial photo-interpretation.
UNIT-II
Physics of remote sensing, Ideal remote sensing system, remote sensing satellites and their data products, Sensors and orbital characteristics, Spectral reflectance Curves, resolution and multi-concept, FCC.
UNIT-III
Satellite Image - Characteristics and formats, Image histogram, Introduction to Image rectification, Image Enhancement, Land use and land cover classification System, Supervised Classification, Applications of remote sensing.
UNIT-IV
Basic concepts of geographic data, GIS and its components, Data acquisition, Raster and Vector formats, topology and Data models, Spatial modelling, Data output, GIS Applications.
UNIT-V
Introduction, Satellite navigation System, GPS- Space segment, Control segment, User segment, GPS satellite signals, Receivers, Static, Kinematic and Differential GPS.
Books:
- 1. A M Chandra: Higher Surveying
- 2. B C Punamia: Surveying & Leveling, Vol 2
- 3. M Anjireddy: Remote Sensing & GIS, BS Publications
- 4. T M Lillesand et al: Remote Sensing & Image Interpretation, Wiley India.
- 5. AM Chandra: Remote Sensing & GIS, Narosa
- 6. S K Duggal: Surveying Vol 2 , TMH
- 7. N K Agarwal: Essentials of GPS, Spatial Networks: Hyderabad.
04 -
JECE-403
Hydraulics and Hydraulic machines:
UNIT-I
Difference between open channel flow and pipe flow, geometrical parameters of a channel, continuity equation. Critical depth, concepts of specific energy and specific force, application of specific energy, principle for interpretation of open channel phenomena, flow through vertical and horizontal contractions.
UNIT-II
Chezy’s and Manning’s equations for uniform flow in open channel flow, Velocity distribution, most efficient channel section.
UNIT-III
Equation of gradually varied flow and its limitations, flow classification and surface profiles, integration of varied flow equation by analytical, graphical and numerical methods, flow in channels of non-linear alignment
UNIT-IV
Classical hydraulic jump, evaluation of the jump, elements in rectangular and non-rectangular channels on horizontal and sloping beds, open channel surge, celerity of the gravity wave, deep and shallow water waves.
UNIT-V
Rotodynamic pumps, classification on different basis, basic equations, Velocity triangles, manometric head, efficiencies, cavitation in pumps, characteristics curves. Introduction of Rotodynamic Machines, Pelton Turbine, equations for jet and rotor size, efficiency, spear valve, reaction turbines, Francis and Kaplan type, Head on reaction turbine, unit quantities, similarity laws and specific speed, cavitation, characteristic curves.
Books:
- 1. Flow through open channel by Subramanya, TMH
- 2. Fluid Mechanics and hydraulic machine by R K Bansal
- 3. Garde, R.J., “ Fluid Mechanics through Problems”, New Age International
- 4. Streeter, V.L. and White, E.B., “Fluid Mechanics”, McGraw Hill, New York.
- 5. Asawa, G.L., “Experimental Fluid Mechanics”, Vol.1, NemChand and Bros.,
- 6. Ranga Raju, K.G., Flow through open channels, T.M.H.
- 7. Rajesh Srivastava , Flow through Open Channels , Oxford University Press
04 -
JECE-404
Engineering Geology:
UNIT-I
General Geology: Branches and scope of geology, Earth, its position in the solar systems, surface features and internal structure, work of natural agencies like lakes, oceans, atmosphere, wind, streams, sea, glacier, Earth movements,Types of weathering, mountains and mountain building, Mineralogy: Definition of crystal and a mineral, the study of the physical properties and occurrence of quartz, Feldspar, Mica, kainite, calcite, tale, corundum, gypsum, fluorite, biotite, mus, covite, graphite, realgar, magnetite, limonite, pyrite, galena, barite, dolomite, garnet, tourmaline, chal-copy-rite, opal, topaz, autite, hornblende, epidate, kaolinite, diamond.
UNIT-II
Petrology: Formation and classification of rocks into three types, Igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rock,description of physical properties for constructional purposes of granite, pegmatite, dolerite, gabbzo, basalt, sandstone, conglomerate, breccia, limestone, shale, schist, marble, quartzite, khondalite, slate, gneiss, andesite, stratigraphy of India (a general idea), principles of correlation, fossils, their preservation and significance. Structural geology: Strike and dip, out crops, volcanoes, overlaps, inliers and outliers, types classification of folds, faults, joints, unconformities.
UNIT-III
Engineering Geology: Ground water, zones of ground water, water table and perched water table, water bearing properties of rocks, occurrence of ground water, springs, selection of a site for well sinking and ground water investigations. Earthquakes and landslides: Classification, causes and effects of earthquakes and landslides, seismic curve, seismographs, seismograms, accelograms, seismic problems of India, seismic zones of India, remedial measures to prevent damage for engineering structures, case histories.
UNIT-IV
Geological investigation: Interpretation of geological maps, use of aerial maps in geological surveying, Geophysical methods as applied to civil engineering for subsurface analysis (Electrical and Seismic methods). Geology of dams and reservoirs: Types of dams, requirements of dam site, preliminary and detailed geological investigations for a dam site, important international and Indian examples of failures of dams and their causes, factors affecting the seepage and leakage of the reservoirs and the remedial measures, silting of reservoirs.
UNIT-V
Rock mechanics and tunneling: Purposes of tunneling and geological problems connected with tunnelling, geological considerations in road alignment, roads in complicated regions, and problems after road construction, geology of bridge sites.
Books:
- 1. Engineering Geology, Parbin Singh
- 2. Engineering Geology, P.K. Mukherjee
- 3. Mineralogy, Dana
- 4. Structural Geology, H.P. Billings.
- 5. B S Sathya Narayanswami, “Engineering Geology”, Dhanpat Rai & Co.
04 -
JECE-451
Structural Analysis Lab:
- 1. To determine Flexural Rigidity (EI) of a given beam.
- 2. To verify Maxwell’s Reciprocal theorem.
- 3. To find horizontal thrust in a three-hinged arch and to draw influence line diagrams for horizontal Thrust and bending moment.
- 4. To find horizontal thrust in a two hinged arch and to draw influence line diagrams for horizontal Thrust and bending moment.
- 5. To find deflection of curved members.
- 6. To find bar forces in a three members structural frames with pin jointed bar.
- 7. To find Critical load in Struts with different end conditions using C.C. and S.C. tests.
02 -
JECE-452
Geoinformatics Lab:
- 1. Demonstration and working on Electronic Total Survey Station (TC-1800)
- 2. To layout a precise traverse in a given area and to compute the adjusted coordinates of survey stations
- 3. Demonstration and working with Pocket/ Mirror stereoscopes, Parallax bar and Aerial photographs
- 4. Visual Interpretation using IRS false colour composite
- 5. Demonstration and practice work with hand held GPS (GS-5).
02 -
JECE-453
Hydraulics and Hydraulic Machines Lab:
- 1. To determine the Manning’s coefficient of roughness ‘n’ for the bed of a given flume.
- 2. To study the velocity distribution in an open channel and to determine the energy and momentum correction factors.
- 3. To study the flow characteristics over a hump placed in an open channel.
- 4. To study the flow through a horizontal contraction in a rectangular channel.
- 5. To calibrate a broad-crested weir.
- 6. To study the characteristics of free hydraulic jump.
02 -
JECE-454
Engineering geology Lab:
- 1. To identify different types of rocks
- 2. To locate the weak plane in the rock.
- 3. To perform hardness test on different rocks.
02 -
JGP-401
General Proficiency
02 -
Total Credits30
